The hiring of foreign citizens with a residence permit in 2020 was finally regulated a long time ago. But employers often still try to draw up any additional documents in order to accept a foreigner, while protecting themselves from questions from the Main Directorate for Migration and Migration (FMS). What rights does the newly hired citizen have and what should the future employer do?
What is a residence permit
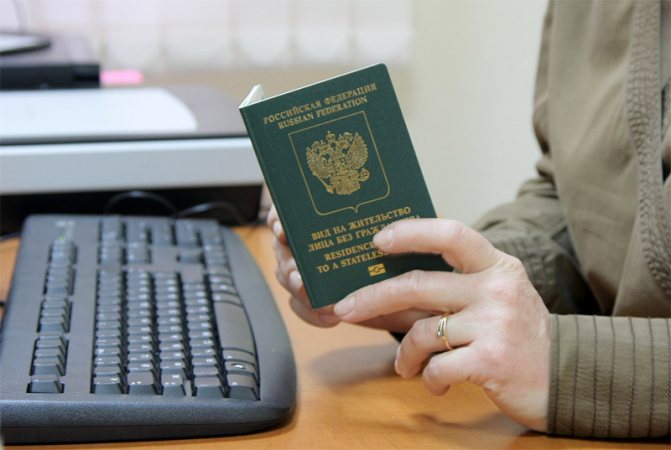

Such documents confirm a person’s right to life within the country, to receive freedoms, guarantees, benefits, and to freely cross the state border. A residence permit in 2021, issued by the Main Directorate for Migration and Migration (FMS), is also an identification document for stateless persons. It has legal force for five years, after which it loses it. When the period comes to an end, a foreign citizen (stateless person) has the opportunity to renew his residence permit at the Main Directorate for Migration and Migration (FMS) of Russia. The migration authority must accept an application for extension at least 60 days before the expiration date. As a rule, there are no obstacles or restrictions. The law states that documents in 2021 can be renewed an unlimited number of times.
Procedure for issuing a residence permit

How does a foreigner have the opportunity to obtain a residence permit? Foreign citizens or stateless persons have the right to obtain a residence permit if they have lived in the Russian Federation for at least one year on the basis of a temporary residence permit, also obtained through the Main Directorate for Migration and Migration (FMS).
A number of foreign citizens can obtain a residence permit without even going through the stage of living in the Russian Federation for a year. These provisions are regulated by the principles of international law and treaties between states. This category includes residents of Belarus, Tajikistan, as well as Ukrainian refugees. A simplified option for purchasing a residence permit in 2021 is provided for stateless persons living in Turkmenistan. The basis for these privileges is the Agreement on the Protection of the Rights and Freedoms of Migrants.
Exemption from obtaining a residence permit

The previously mentioned Federal Law establishes a list of those categories of foreign citizens who are not required to obtain any permits in order to carry out a certain type of labor activity:
- employees of representative offices and embassies;
- composition of the diplomatic mission;
- employees of international organizations;
- journalists accredited to work in the Russian Federation in 2021;
- citizens of foreign countries receiving secondary or higher education in the Russian Federation (by the way, they can work in their free time);
- participants of the State Program for the Resettlement of Compatriots Living Abroad;
- teaching and research staff applying for work in Russia;
- official representatives of products manufactured abroad, suppliers (if necessary, installation, adjustment of equipment, servicing of goods under warranty).
Official employment under a residence permit

Legal employment is carried out using a work book. But a lot depends on the status that a foreign citizen has in 2021.
A person can be employed in a position in the same manner as a full-fledged Russian. He is provided with the entire range of social guarantees.
Foreigners who have received a residence permit do not receive from the Main Directorate for Migration and Migration (FMS) of the Russian Federation any permits confirming the ability to legally work in the country. When hiring a foreign citizen, the employer undertakes the obligation to notify the Main Directorate for Migration and Migration (FMS) about this.
Features of hiring a foreigner with a residence permit
There are certain nuances when hiring foreigners. They are provided for in Art. 13 of Law No. 115-FZ of July 25, 2002. In particular, they are required to have a work permit and a patent.
But these restrictions do not apply to holders of residence permits and temporary temporary residence permits, participants in the compatriot resettlement program, foreign journalists, diplomats, consuls, full-time university students and some other persons. This is the main feature of hiring a resident with a residence permit.
When working, a non-resident with a temporary residence permit is also required to have a voluntary health insurance policy or a service agreement with a private clinic. A foreigner with a residence permit may not comply with this requirement and apply for compulsory medical insurance.
Official employment
A foreigner has the right to be officially admitted to the employer's staff. This means that he is fully covered by labor laws.
Namely:
- A new work record book is created for the foreigner or an old one is filled out and the employment order is approved.
- If the company is a participant in a salary project with a bank, then a salary card is also issued. Banks are ready to issue and service cards for foreigners with a residence permit.
When hiring, the employer is obliged to check the documents of a foreigner and make sure that his residence permit is not expired, and registration does not end in a couple of days. Otherwise, the employment procedure is the same as for Russians.
Employment contract with residence permit
An employment contract can only be concluded with a foreigner over the age of 18. The text of the agreement must contain information about the employee’s residence permit (number and other information similar to the passport data of a Russian citizen).
Interesting article: Online registration for a residence permit: how and where to sign up?
An employment contract with a foreigner with a residence permit is drawn up for an indefinite period or for a certain period. Registration takes place in written or oral form. If the agreement is oral, then the employer is obliged to notify the Main Migration Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. This must be done within three days. Download a sample notification here.
The employing company is also obliged to notify the Main Department of Migration Affairs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs about the dismissal of an employee and about the payment of his salary (a fee under a civil contract), if he is a highly qualified specialist.
Documentation to be presented

When applying for a job, a person must present at the place of employment the documents specified in part one of Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with a number of exceptions.
- It is irrational to demand documents on military registration, since foreigners are not obliged to perform military service in Russia.
- In order to conclude a contract, you need to issue a SNILS. If a person does not have this number, the employer must independently arrange for it.
- In addition to the papers specified in the Code, a migration card is required, which is issued and filled out at the border, upon its first crossing.
- The employer must be notified of whether the type was legally acquired (on the appropriate form established by law) and whether it is valid today.
- A fixed-term or open-ended contract is concluded in accordance with the provisions of Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Civil contracts for the performance of any work or provision of services are signed in accordance with civil law.
- An order or instruction on hiring and familiarization with it to an employee according to the rules of 2021 is carried out no later than three days after the start of work.
- If there is no work experience in Russia or countries that were part of the Soviet Union, and as a result, a work book of the 2002 (1974) model, the employer must issue it when hiring.
Entries can only be made in Russian documents; accordingly, work books of a foreign country are not used, as this is prohibited by law.
- Employment in 2021 involves issuing a personal card for a foreigner.
- The GUVM (UMFS) of Russia must be notified of the hiring of an employee within three days. Otherwise, Article 13 of Federal Law No. 115 is violated.
The Federal Migration Service was abolished in April 2021. The body that replaced it was the Main Directorate for Migration Issues of the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs.
Who resolves disputes between the parties?
If a foreigner decides to sue an employer over refusal to hire, non-payment of wages or for other reasons, then he has the right to go to court.
Interesting article: Does purchasing real estate in Russia affect obtaining a residence permit?
A complaint against an employer can also be filed with the labor inspectorate. They are required to check within a month whether the employee’s rights have been violated or not. If the employer pays the salary “in an envelope”, i.e. informally, you can also contact the tax authorities.

All issues related to labor disputes are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Its effect applies to all foreigners. The employment contract itself with a foreigner is also important.
Features of building labor relations
The category of foreigners permanently residing in the Russian Federation (on the basis of a residence permit) are automatically recognized by the tax authorities as residents of the country, since they are in Russia for more than half of the year. Accordingly, they are required to pay income tax (rate - 13%) on wages.
Foreigners who regularly stay within the country fall under the definition of the category of insured persons. Based on the law, they are required to make insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds for compulsory medical, social and pension insurance every tax period.
Thus, in 2021, the employer and employee are not required to complete additional papers or requests. And the often encountered unofficial hiring of foreigners is simple illiteracy in the legal field or reluctance to draw up a contract in a standard manner.
What are the consequences of violating labor laws?
Violation of the regime for hiring foreigners can provoke big problems. They are especially dangerous in the capital and St. Petersburg, where the amounts of fines are much higher than in the regions.
Interesting article: Residence permit - what is it and how to get the document?
To the employer
Employers are subject to large fines for violating the requirements of the law on the employment of foreigners. The size of sanctions can reach a million rubles and lead to the suspension of activities for a period of several weeks to three months.
Sanctions are provided for:
- failure to notify a foreigner of employment (up to 800 thousand rubles in the regions, if in the capital and St. Petersburg, then up to 1 million rubles);
- failure to comply with restrictions for non-residents when carrying out certain types of activities (up to 1 million rubles);
- providing false information about a foreign employee of the Main Directorate for Migration Affairs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (from 350 to 800 thousand rubles).
Fines in the event that a person with an unextended residence permit or no documents is employed are levied on both legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. But for individuals the fines are less (from 5 to 7 thousand rubles).
A foreigner with a valid residence permit, but with expired registration, is considered an illegal immigrant and is also subject to sanctions for his employment.
To a foreigner
Sanctions for violating the procedure for employing foreigners are mainly borne by the employer. The migrant himself is responsible only for having a residence permit (without expired dates or forgeries), as well as registration (temporary or permanent).
He also needs to annually notify the Main Directorate for Migration Affairs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs about his place of residence, income and place of work. If you violate this requirement, then a fine of up to 2-7 thousand rubles is possible, and in case of malicious violation: cancellation of the residence permit status.
If a foreigner decides to work without official employment, he may face a fine of 5 thousand rubles and even deportation.