Latvia belongs to the countries of the European Union, accordingly, many Russians are considering options for earning money abroad in this country.
Riga is the largest city in Latvia
They are interested in such important details as salaries in Latvia, which professions are most in demand, what the minimum and average cost of living is currently set according to statistics, so that you can understand what to expect. You also need to know what the pros and cons of living in this country are for a Russian, and how easy it is to find a job here.
Salary level in Latvia
As of January 2021, no more than 0.7% of the population lives below the poverty line. Indicators of average earnings vary from the characteristics of the employer's institution, the specialty and work experience of the employee, his place of residence, age and gender. During the period from 2017 to 2021. There is a gap between the average and minimum earnings. So, if in 2021 the average salary exceeded the minimum wage by more than 2 times, then by the beginning of 2021 this difference had decreased to 40%.
Minimum
The legal minimum wage (SMW) as of 2021 is €430 per month or €2.48 per hour when working 40 hours per week. The employer is prohibited from lowering this level. Currently, 16.9% of Latvians receive the minimum wage.
Average
In Latvia, there is a so-called average starting salary, which is approximately 25% lower than the salary of a specialist who has worked at the company for a long time. Foreigners working in the country receive an average of €600-800.
The average salary in the country varies between €700-1400. About 25.7% of the population receives it.
Maximum
The maximum earnings are directly dependent on the specialty and qualifications of the employee, as well as on the intensity of his work. In the information technology sector, the salary can exceed €3,000, reaching €3,000-5,000 for the CEO. The maximum salary for lawyers is €1,700, for salespeople – €800.
The highest paying professions
In order to determine how much you can earn in Latvia, you must also take into account vacancies that pay well. If you look at the salaries of specialists, you can get more complete information about how much they earn in Latvia.
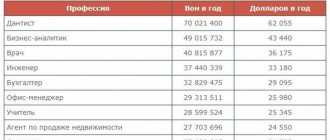
Income of the population of Latvia by profession:
- A doctor’s salary ranges from 1100 to 1700 euros per month;
- Nanny salary – 700 – 800 euros;
- Worker's salary – 400 – 800 euros;
- Teacher’s salary – 600 – 1000 euros;
- Welder salary – 800 – 1200 euros;
- The salary of firefighters is 1000 - 1300 euros.
Above are the conditional incomes of Latvian residents. It should be understood that in order to obtain more accurate information, it is necessary to take into account experience, responsibilities and qualifications. In addition, the income of citizens also depends on the capabilities of the company.
The average salary in Latvia in 2021 is 740 euros.
Dependence of wages on specialty and industry
The highest paid categories of the population include doctors, with an average salary of €1100-1700 (dentists - €1400), firefighters with a salary level of €1000-1300 and programmers, whose average income is €1200-2500. The average salary of teachers is in the range of €600-1000 (60 thousand rubles).
The lowest wages are for waiters - €450-650, nurses - €650-750, workers - €400-800 and salespeople - €500-800.
As of early 2021, employees of state-owned companies are paid slightly more for their work than their private sector counterparts.
The annual increase in average earnings is approximately 6-8%. At the same time, the dynamics of changes vary depending on the specifics of work activity. Workers in the chemical, pharmaceutical and insurance industries experienced the highest income growth. In the transport sector, on the contrary, there is a decline.
Communication services on the territory of the Republic of Latvia
Modern, high-quality communications throughout the country are what Latvia can truly boast of. The local landline telephone service, fully digitalized with an eight-digit number system, has approximately 700,000 subscribers. About 65% of the country's population receives fast Internet services. In addition, the Latvian cellular communications market is actively developing.
Fixed telephone services are provided by the state enterprise Lattelekom. As for cellular communications, the country is almost completely covered by the networks of three main operators: LMT, Tele2 and Bite. All mobile operators in Latvia offer 4G mobile internet to their customers. Tourists can use local prepaid cards, which can be easily purchased at any supermarket, mobile phone store or kiosk. The starter kit costs about 5€ - it will be enough for a few days of vacation. At the same time, you can use the Internet for free via WiFi in any public place.
Are there differences in salaries by region?
According to statistics, residents of Riga earn on average 15% more than residents of other localities and cities, while the salary of men is approximately 15-20% higher than the salary of women. In numerical terms, the salary of Riga residents is €1042, in the Riga region it is slightly lower - €1004, in Vidzeme, Kurzeme and Zemgale - €720-765. The lowest average earnings among residents of Latgale are €622. However, the average salary growth in Riga is slightly lower than in other regions. At the beginning of 2019, it amounted to just over 7% (€69 compared to 2017).
Hot vacancies and salary statistics for 2021
Latvia ranks last among all EU countries in terms of level of security. Salaries in the country in 2021 became slightly higher than in the past, but still, this did not change the overall picture much.

At the moment, according to statistical calculations, the minimum wage in Latvia in 2021 was 430 euros per month. The average salary is 1091 euros per month. Salaried workers receive less only in Lithuania, Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria.
The most common and available vacancies for Ukrainians, Russians and Belarusians in Latvia:
- international drivers,
- truckers,
- builders,
- engineers,
- workers in the field of computer technology.
Wood workers, pharmacists, and social workers are less often required. Typically, salaries for these specialties are a little more than 1000 euros.
A special place is occupied by “unskilled” professions; they are also of interest to residents of post-Soviet countries - nurses, housekeepers, waitresses, hostesses, loaders, salespeople, assistant cooks, nannies. There is seasonal employment in Latvia in the agricultural sector for harvesting, but the earnings here are poor, no more than 500–600 euros per month, if not less.
Seasonal work in Latvia
Income statistics (ascending):
- Managers, salespeople - 1100–1400 euros per month.
- Construction project managers - 1–1.5 thousand euros.
- Marketers - 1–1.5 thousand.
- Auditors, chief accountants - 1–1.8 thousand.
- Programmers and system analysts - 1–2.5 thousand.
- Company managers - 1100–7200 euros.
As for salaries by region, the cost of living and the average are approximately the same everywhere, but special mention should be made of earnings in the capital of the country, Riga.
Salaries in Riga are the highest, about a quarter higher than in other cities, but prices for everything have been increased by the same amount.
So, where to start working, you need to decide carefully.
The tax system in Latvia and its impact on wages
Citizens and residents are required to pay taxes. Residents include persons staying in the state for more than 183 days a year. Non-residents are required to pay taxes only if they receive earnings in Latvia. The total tax burden is one of the highest among the European Union (EU) countries and amounts to 35%.
The tax system is progressive with a dominant income tax rate of 23%, which covers the population group with an annual gross income of €20,005-55,000. With an annual income of less than €20,000, the bar is reduced to 20%; if it increases above €55,000, it increases to 31.4%. The law obliges the employer to transfer tax payments to the budget.
In addition to income tax, socially significant payments include: road tax, as well as taxes on inheritance and real estate, as well as those paid upon the sale of real estate. Social insurance contributions will be distributed between the employee - 11% and the employer - 24.09%. Tax rates vary for different categories of the population.
Income tax is withheld after social contributions are withheld.
Until 2021, when earning less than €440, the law provided for a tax-free minimum of €200. In 2021, as a result of social changes in legislation, the non-taxable income tax minimum for workers with low earnings or with dependents was increased to €230, and for persons receiving a pension – to €270. Also, students receiving scholarships up to €280 do not pay income tax. In Latvia, the maximum annual tax-free minimum cannot exceed €4,800.
To simplify the calculation of income in the country, a net salary calculator is used.
Sometimes they come back
How does rising wages affect competitiveness and emigration? The level of income in Latvia lags behind the level of income in Western European countries, which encourages many to go in search of better paid work outside our country. For this reason, rapid wage growth and moving closer to the average income level in the European Union are highly desirable goals.
There are signals indicating that the emigration flow is gradually subsiding.
However, on the other hand, if we run too fast and wages grow faster than labor productivity, we can shoot ourselves in the foot, fears Agnese Buceniece.
A disproportionate increase in wages threatens competitiveness and could negatively affect our ability to export, which means a decrease in income.
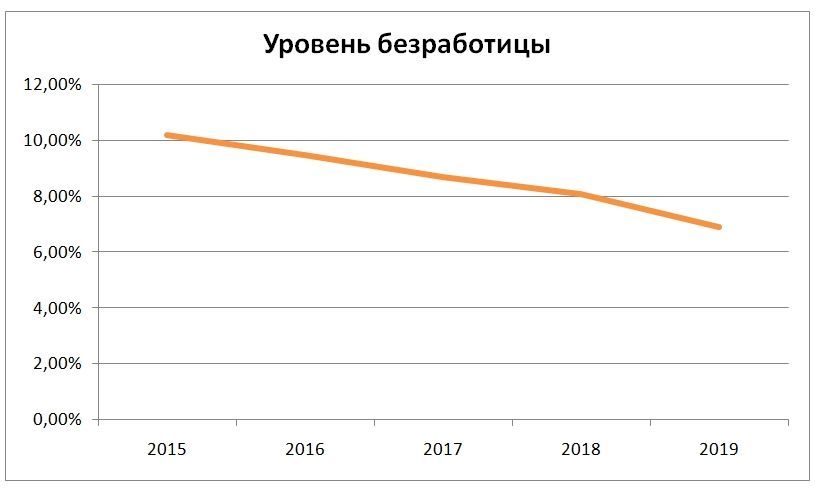
Unemployment in Latvia
According to statistics, the unemployment rate in the country from 2015 to the beginning of 2021 decreased from 10.2% to 8.1%. At the end of 2019, this figure was 6.9%. The highest proportion of unemployed people is among young people – 10.8%.
The lowest unemployment rate among the working population in Riga is 4%.
According to forecasts, the share of unemployed in 2021 and in subsequent years will steadily decrease by 0.2-0.3% per year.
Prospects for migrants in Latvia
A relatively high standard of living, combined with the situation on the labor market, creates favorable conditions for migrant workers, especially workers and seasonal workers (for picking berries on berry plantations), as well as those sectors of the economy where earnings for the local population are considered the lowest. Such professions include drivers, salespeople, support and maintenance personnel. Builders, engineers and programmers from Belarus, Ukraine and Russia are especially valued.
Legislatively, the employer is given the right to employ a foreigner, provided that none of the indigenous residents of the republic have responded to this vacancy. In this case, the applicant must have an invitation from the employer. Having hired a foreigner, the employer is obliged to inform the state employment tracking service (GAS) about his decision in order to monitor possible applicants for this vacancy from the local population. This is one of the forms of combating unemployment in Latvia.
Exceptions to this rule are: EU Blue Card holders, self-employed and entrepreneurs, arts and sports industry workers, international contract specialists, foreign teachers with special accreditation.
To qualify for a high salary, an immigrant candidate must meet the following requirements: knowledge of the Latvian and English languages, possession of a higher education (a diploma must be obtained in one of the EU countries or recognized in these countries), have a residence permit and a work permit in the EU.