What is citizenship
The etymology of the definition of “citizenship” has ancient Greek roots. Initially it was defined as a person living in a settlement or city. In its modern meaning, the word began to be used in the middle of the 18th century. During this period, the Russian prose writer and statesman of the times of Catherine II A.N. Radishchev used this concept as “a person who belongs to the population of a particular state.”
Citizenship implies a legal relationship, a connection between a person and the state, defining the rights and obligations of each party. They are prescribed in the Constitution of the country, its other legislative and regulatory acts.
The state is obliged to provide:
- protection, regardless of the actual location of a person at a certain moment;
- legal and social security;
- equal opportunity to participate in the political, economic and social life of the country;
- other rights.
A citizen of the Russian Federation has responsibilities and rights
The citizen, in turn, is obliged:
- comply with current legislation;
- defend the principles and foundations of the state;
- prevent harm to the state and attacks on its constitutional order, etc.
Initially, the status of a citizen of a state is determined at birth - according to the parents’ belonging to a particular country, their nationality, etc. During his life, a person has the opportunity to change citizenship, or, if the laws of the country allow, to obtain a second one. This possibility, as a rule, exists in the event of the conclusion of relevant agreements between two countries. At the same time, a person who has received the status of a citizen in several countries bears an obligation to each of them, while receiving its own preferences.
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation:
- all citizens of the Russian Federation have equal rights and obligations, regardless of the receipt procedure;
- a document certifying a citizen’s citizenship is a PASSPORT;
- there is a legal possibility of obtaining a second citizenship;
- even a person’s long stay outside the country is not grounds for deprivation of citizenship, etc.
Who can count on a simplified procedure
The option of how to quickly obtain Russian citizenship provides for some relaxations only in the issue of length of residence on Russian territory. All other procedures and formalities remain mandatory.
To become a Russian citizen, bypassing the general procedure, first of all, individuals who were somehow connected with the USSR, the RSFSR or the Russian Federation have the opportunity to become a Russian citizen.

These include:
- Persons born on the territory of the Russian Soviet Republic.
- Citizens of the USSR.
- Persons who lived on the territory of the USSR on the basis of permanent residence.
- All those whose father or mother are Russian citizens and permanently reside on the territory of the state.
Acquiring Russian citizenship in a simplified manner is also possible, based on family circumstances, for the following migrants:
- disabled people and people of retirement age whose children are capable and can confirm their Russian affiliation;
- persons who have a child who is a citizen of the Russian Federation and has not yet reached the age of majority, in the absence of a second parent;
- those who are married to a Russian citizen and have children together.
Specific categories of citizens can be included in a separate group:
- WWII veterans;
- children, disabled people, pensioners who are supported by Russian citizens;
- participants in a program promoting the resettlement of compatriots;
- residents of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova;
- refugees.
The changes made to date have significantly simplified the legalization procedure for the following persons:
- Those who, after 2002, became the holder of an education diploma issued by a Russian educational institution and worked in their specialty for at least three years.
- Individual entrepreneurs whose business has been operating in the Russian Federation for at least three years and generates an income of 10 million rubles annually.
- Owners of 10% in the authorized capital of Russian companies.
- Specialists who have worked in the country for three years in one of the professions indicated in the list of in-demand professions.
The period for obtaining Russian citizenship under a simplified procedure is six months (for all others – a year). For native speakers and participants in the resettlement program, this period is reduced to three months.

All of these categories of candidates must prove that they speak Russian, respect and know the culture of the Russian people, have Russian relatives or have some kind of relationship with the country as a whole.
For the final legalization procedure, renunciation of previous citizenship is mandatory.
Legalization algorithm
The stages of obtaining Russian citizenship in a simplified manner can be outlined as follows:
- Crossing the state border. Filling out a migrant card.
- Registration of stay on Russian territory seven days after entry.
- Temporary residence permit. Issued for a three-year period without the right of extension. An indispensable condition for obtaining is having a place of residence. The application is being considered for two months. For Belarusians, this stage is excluded from the list of mandatory ones.
- Resident card. Issued for five years. Subject to extension. To obtain it, you must confirm your source of income and place of residence.
- Citizenship. Requires confirmation of knowledge of the Russian language.
Only pensioners, incapacitated persons, minor children and residents of countries where Russian is also the state language will be able to avoid testing for knowledge of history, laws and the Russian language.
Obtaining citizenship
According to the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, it is possible to obtain citizenship in the following cases:
- By birth. A child automatically becomes a citizen of our country if, at the time of his birth:
- the mother and father have the status of Russian citizen, and the place of birth of the child does not matter;
- one of the parents is a citizen of the Russian Federation, and the second is a citizen of another country/has no citizenship/his location is unknown. Also, place of birth does not matter;
- both parents are foreign citizens living in the Russian Federation, provided that the child is born in Russia and another state refuses to grant the child the rights of a citizen;
- none of the parents was found within six months from the moment the child was discovered (abandoned children).
- Upon restoration of citizenship. If a person previously had Russian citizenship and renounced it (according to his own statement), he subsequently has the opportunity to restore his status on the territory of the Russian Federation.
- Admission to citizenship. It is possible in compliance with the usual or simplified scheme (we will consider further).
- Other reasons. In accordance with domestic legislation and international treaties of Russia.
Let's consider the main requirements put forward by law for applicants for civil status in Russia under the simplified system. As well as exceptions that are allowed from the basic rules.
Grounds for simplified acquisition of citizenship
Previously, an exhaustive list of grounds for obtaining a Russian passport under a simplified scheme was presented in Article 14 of the citizenship law. Amendments to the document added one more condition:
- you must belong to the category of foreigners, the list of which is determined personally by the President (clause 1.1 of Article 29 No. 62-FZ).
Such persons may not meet other criteria established by Article 14 of the Law on Citizenship, and at the same time retain the right to receive a passport in a simplified mode (clause b) of Part 1 of Art. 1 No. 544-FZ).
Which specific persons will fall into this category will be determined by additional Decrees of the President of the Russian Federation. At the moment, one such document has been published (dated April 24, 2021).
Requirements for obtaining Russian citizenship

To obtain a passport you need to fulfill a number of conditions
A person who plans to obtain the status of a Russian citizen must meet a number of conditions specified in the Federal Law:
- First of all, the “candidate” must actually reside in the territory of our country and must have a so-called residence permit. An exception to this rule may be persons (foreign citizens or those without any citizenship) who live outside the Russian Federation. They must submit an application for obtaining the status of a Russian citizen to the authorities of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (consulates, diplomatic missions) abroad. Such persons must meet the requirements established for obtaining citizenship under the simplified scheme.
- If you actually reside in the territory of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, you must have permanent registration at your place of residence.
- Be employed and, accordingly, have legal sources of income.
- Initiate the procedure for depriving the currently existing citizenship of another power.
- Have sufficient command of the spoken and written state language. The exceptions are:
- elderly people (for women - from 60 years and older, for men - from 65 years);
- recognized, in accordance with the established procedure, as incompetent;
- disabled people of group I.
The procedure for obtaining citizenship under a simplified system
Current legislation provides for the issuance of a special visa, the purpose of which is to obtain Russian citizenship, as well as the possibility of freely obtaining a residence permit.
In order to prevent abuse, a residence permit may be revoked from an applicant if, after 2 years, he does not submit an appropriate application for admission to Russian citizenship.
Thus, the simplified procedure eliminates the need to obtain a temporary residence permit on the territory of the Russian Federation, and, consequently, to live under it for at least a year before receiving a residence permit. The list and form of documentation required to obtain citizenship in a simplified manner remains the same:
- personal statement of the applicant in two copies;
- passport of a citizen of the USSR with a mark of registration at the place of residence/document of a relative, or an identity document of a citizen of a foreign state or a stateless person, temporary residence permit/residence permit with a mark of registration at the place of residence + copies of documents;
- a document confirming the applicant’s place of residence;
- a document ensuring that the applicant/his relative has USSR citizenship or the fact of residence in the Russian Empire in the past;
- documents proving the fact of change of surname, name, patronymic, if any, + their copies certified by a notary;
- a notarized application for renunciation of existing citizenship or another document confirming the fact of the applicant’s application to renounce existing citizenship of a foreign state;
- three photographs of an applicant for Russian citizenship (size 3x4);
- documents confirming the fact of payment of the state duty (stateless persons who have such status as a result of the collapse of the USSR and failure to obtain citizenship of other states that were part of the USSR do not pay the state duty).
The right to obtain Russian citizenship in a simplified manner
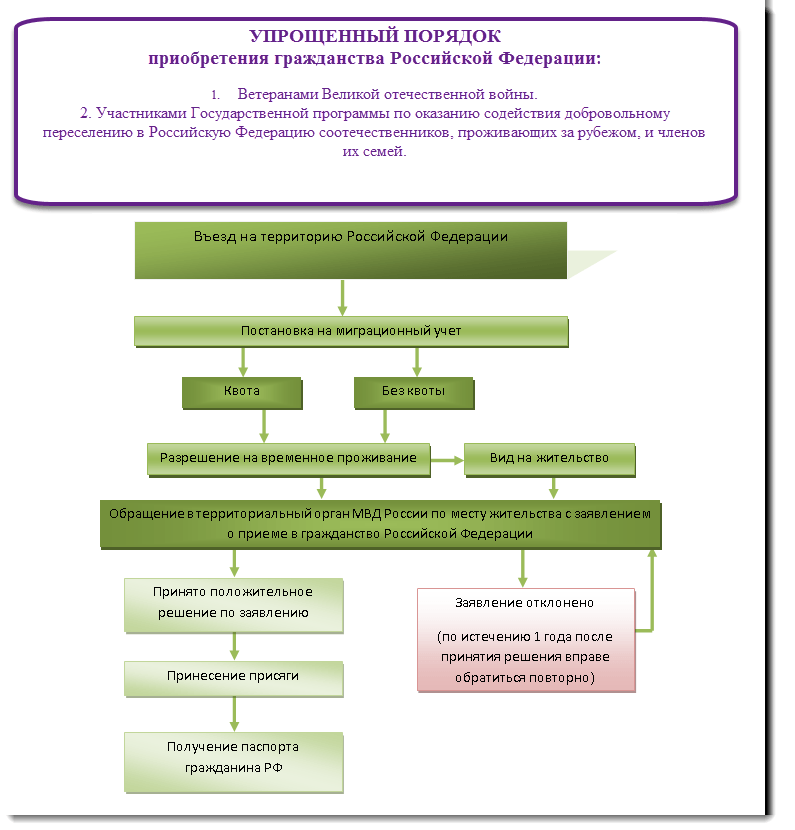
Simplified procedure for obtaining citizenship
So, we have come to the most important question - which category of people can apply for the legal status of a citizen in Russia under a simplified scheme. And also, what are the exceptions and “benefits” provided for by the Law “On Citizenship”.
The rules for the simplified granting of citizenship are contained in Article 14 of the said Federal Law, which stipulates an exhaustive list of foreign nationals and stateless persons. Possibility of receiving such a “benefits”.
Table. Categories of applicants who are given the opportunity to obtain simplified status of a citizen of the Russian Federation.
Capable, adult (18 years of age and older) citizens of other states, as well as those who do not have the latter in any country, in cases where:
| No. | Article 14 of the Federal Law of May 31, 2002 No. 62 (in the current version - hereinafter referred to as the Law) | Category of persons who have preferences for obtaining citizenship under a simplified scheme | Note |
| 1.1. | part 1, paragraph "a" | - parents (or one of the parents) have Russian citizenship and live in the Russian Federation. | It is necessary to focus specifically on the actual residence of the person’s mother/father in the territory of one of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. There must be documentary evidence of the parent's registration at the place of residence. |
| 1.2. | part 1, point "b" | - a person was a citizen of the Soviet Union before the “collapse” of the Soviet Union, and currently lives on the territory of one of the former republics of the USSR. At the same time, without obtaining citizenship of the new state. | The “pitfall” of this norm is the absolute absence of any civil status for a person after citizenship of the USSR. Those. If a person during this period acquired citizenship of any country and then lost it for any of the possible reasons, he loses the opportunity to apply this rule of the simplified version and switches to the general procedure. |
In accordance with the paragraph considered, the legislation does not establish a requirement for compulsory residence in the territory of our state of the applicant. The application can be submitted both in Russia and at any consulate (diplomatic mission) of Russia outside its borders. In addition, when submitting an application abroad of the Russian Federation, a document (permit, type) giving the right to reside in Russia is not required.
Citizens of other states (or who do not have one in any country) permanently residing in Russia, in cases where:
| No. | Article 14 of the Federal Law of May 31, 2002 No. 62 (in the current version - hereinafter referred to as the Law) | Category of persons who have preferences for obtaining citizenship under a simplified scheme | Note |
| 2.1. | part 2, paragraph “a” | — was a citizen of the former USSR. Moreover, the place of birth was a territorial unit that was part of the RSFSR. | |
| 2.2. | part 2, point "b" | - the spouse has the status of a citizen of Russia, and the duration of the marriage is at least 3 years. | |
| 2.3. | part 2, point “c” | - there is a status of a disabled person, while children (or 1 child) who have reached the age of majority (18 years) are capable citizens of Russia. | |
| 2.4. | part 2, paragraph "d" | - the son (daughter) is a citizen of the Russian Federation, and the second parent: * has been determined by the court to be missing; * is incapacitated (partially incompetent); * deprived of rights to the child by the court; * died. | |
| 2.5. | part 2, paragraph "e" | - the son (daughter) has reached the age of 18, is a citizen of the Russian Federation, and has been declared legally incompetent. And the second parent: * determined by the court as missing; * is incapacitated (partially incompetent); * deprived of rights to the child by the court; * died. | |
| 2.6. | part 2, paragraph "e" | — received vocational education in Russia after the Law came into force and worked in the country for at least 3 years. In this case, the educational institution must have a state license. accreditation, and the employer has paid all due insurance premiums in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. | Persons who worked in Russia “illegally” and receive payment in “envelopes” lose the opportunity to apply this rule. |
| 2.7. | part 2, paragraph "g" | — engage in business activities in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation. Continuous period – 3 years or more. At the same time, the annual amount of taxes and fees paid to the budget is more than 1 million Russian rubles. | When determining the total amount of payment, taxes are not taken into account: land, transport, personal property, duties, and overpaid amounts. |
| 2.8. | part 2, paragraph "h" | — carry out investment activities in sectors of the state economy. At the same time, contributions to the capital of a Russian enterprise range from 10% (but not less than 10 million Russian rubles) and did not fall below this figure continuously for 3 years before the filing of the application. And the annual amounts of transfers to the budget of taxes and fees exceed 6 million Russian rubles. | When determining the total amount of payment, duties, as well as overpaid taxes and fees, are not taken into account. |
| 2.9. | part 2, paragraph “and” | - for at least 3 years before submitting the application, they worked in the Russian Federation in a specialty that is included in the List of professions that give the right to admission under a simplified procedure. This procedure was approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of July 13, 2015 N 446/n. At the same time, during the entire period the employer is obliged to pay insurance premiums for this employee. | The list specifies 74 specialties of technical and medical workers who receive benefits for simplified citizenship. Work in other professions does not give the right to use this norm. |
| 2.10. | part 2.1 | - recognized, in the manner prescribed by law, as “native speakers of the Russian language.” The recognition procedure is stipulated by Article 33.1 and provides for: * filing an application within the time limits specified by the Law to the Commission for recognizing a person as a “native speaker of the Russian language”; * application deadlines for persons temporarily staying in the state - at least 15 days before the end of the period of stay, for residents - 3 months before the end of the period of stay. * undergoing an interview with the Commission, based on the results of which a decision is made. The validity period of a certificate confirming that a person is a “native speaker” is unlimited. | Persons recognized as “native speakers” are obliged to: - comply with the norms of Russian legislation; - have legal income; - renounce the citizenship existing at the time of filing the application. An exception may be cases where such a refusal is impossible due to reasons beyond the person’s control. Refusal is carried out by submitting a personal statement to the authorized body of such state. The supporting document is a copy of such application certified by a notary. In addition, a person is required to register (permanent or temporary) at his place of residence in one of the constituent entities of the Federation. |
For persons corresponding to this paragraph, there is already a norm that obliges them to reside in the territory of our country. And documents are submitted exclusively to local authorities of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, which are responsible for the issue of population migration. In this case, a residence permit and permanent registration are required. There are no restrictions on age and legal capacity for this category.
| No. | Article 14 of the Federal Law of May 31, 2002 No. 62 (in the current version - hereinafter referred to as the Law) | Category of persons who have preferences for obtaining citizenship under a simplified scheme | Note |
| 3. | part 3 | Citizens of other states (or who do not have the latter in any country), who have lost their ability to work, who came from the countries of the former USSR and received registration in Russia before the Law in question came into force. | For this category, it is possible to submit an application without fulfilling the condition of mandatory residence in the Russian Federation for 5 years from the date of receipt of a residence permit. |
| 4. | part 4 | Able-bodied citizens of other states (or who do not have the latter in any country), who came from the countries of the former USSR and received registration in Russia before the Law in question came into force. Subject to submission of the relevant application before 07/01/2009. | Currently not relevant due to the expiration of the deadline for submitting documents. |
| 5. | part 5 | Veterans of the Great Patriotic War who had USSR citizenship, subject to residence in Russia. | |
| 6. | part 6 | Children: - mother or father, who is a citizen of the Russian Federation who submitted the application. If the child lives in Russia, the consent of the second parent is not required; - those under guardianship or guardianship based on the request of a guardian; - orphans in orphanages. According to the statement of the head of the relevant institution. | |
| 7. | part 7 | Citizens of other states (or who do not have one in any country) who are participants in the state program for the resettlement of compatriots. | Subject to compliance with the terms of this program. |
Preparatory stage for obtaining citizenship
The conditions and procedure for granting citizenship of the Russian Federation to foreigners are described in the Law “On Citizenship” (FZ-62).
What are the requirements for applicants?
Foreigners who wish to become holders of a Russian passport must:
- know and adhere to the Russian Constitution and other legislative acts of the Russian Federation;
- have legal income;
- receive a renunciation of the citizenship of the state of which they were previously citizens;
- be fluent in the state language of Russia.
The above requirements are established in Art. 13 of the Citizenship Law.

Candidates for citizenship must know and comply with the Russian Constitution
Grounds and conditions for obtaining Russian citizenship in a simplified manner
One of the main conditions for obtaining citizenship according to the general regulations is legal residence in the Russian Federation for at least 5 years in a row in accordance with Article 13. FZ-62. The simplified procedure cancels compliance with this provision in a number of cases, which is reflected in Art. 14. Thus, immigrants can apply immediately without obtaining a residence permit or residence permit. However, there are exceptions.
The main ways to obtain Russian citizenship using a simplified scheme, when preliminary registration of a residence permit or temporary residence permit is necessary:
- Getting married. Citizenship is granted to spouses of Russians who have been married to them for at least 3 years.
- Studying at a Russian university. An immigrant must receive education at one of the higher educational institutions of the Russian Federation under a program that has state accreditation. In this case, you must work for at least 3 years officially in your specialty, that is, during this period you must pay contributions to the Pension Fund.
- Entrepreneurial activity. Individual entrepreneurs or founders of legal entities can also apply for citizenship after 3 years of carrying out their activities. The main condition is that the taxes and fees paid in total must be at least 1 million rubles over 3 years.
- Participation in the State Program to promote the resettlement of compatriots from abroad. Participants in this program are eligible to apply for themselves and their family members as long as they are registered at the residential address in the region they have chosen. There is no need to confirm language proficiency or income.
- Investment. Investments in an enterprise operating in Russia must be at least 10% of the total capital during the 3-year period before filing the application, the total capital of the organization is at least 100 million rubles, and the amount of taxes and fees paid is 6 million.
- Job. Persons who have worked in the Russian Federation for 3 years in one of the in-demand specialties can apply. A mandatory condition is the transfer of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation. The full list of professions can be viewed at the link.

Spouses of Russian citizens can apply for citizenship after 3 years of living together in Russia
The following categories of immigrants can become holders of a Russian passport without obtaining a residence permit:
- holders of passports of Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan and Belarus;
- adults with legal capacity who have at least one parent living in the Russian Federation and holding a Russian passport;
- adults with legal capacity who previously had Soviet passports, but currently live in the countries of the former USSR, but have not obtained citizenship there;
- foreigners born in the RSFSR and who had a Soviet passport;
- disabled parents of capable adult children - citizens of the Russian Federation;
- parents of children with Russian citizenship, including those who are incompetent, if the other parent has died, is missing, is incompetent (fully or partially), or has lost parental rights;
- native speakers of Russian (you must have a certificate of recognition);
- disabled foreigners from the CIS countries, including those without citizenship of any country and former citizens of the Soviet Union, registered in the Russian Federation as of July 1, 2002;
- WWII veterans;
- children whose one or only parent has a Russian passport;
- children and incapacitated persons whose guardianship is provided by Russian citizens;
- orphans and those left without parents, as well as incompetent persons who are under the supervision of government organizations.
According to a simplified scheme, they also acquire Russian citizenship in the order of its restoration.
Video: simplified citizenship for Russian speakers
Documents for obtaining citizenship under an accelerated scheme
To obtain citizenship you will need the following documents:
- 2 copies of the application for acquisition of Russian citizenship completed and signed by the applicant;
- passport;
- 3 photos 3 × 4 cm;
- renunciation of previous citizenship;
- original registration in the Russian Federation;
- documents confirming the basis for obtaining citizenship according to a simplified scheme;
- confirmation of payment of state duty.
You must fill out the application manually or using a computer. Questions should be answered unambiguously and completely. You also need to remember that corrections and reductions are unacceptable. The application form and an example of how to fill it out are available on the Ministry of Internal Affairs website.

Renunciation of citizenship is a mandatory condition for applying for Russian citizenship
If citizenship is issued to a minor, one of his parents is responsible for filling out the application (notarized consent is required from the second). If the child is already 14 years old, he must obtain written consent to become a citizen. The signature can be certified by a notary or a migration service employee when submitting documents.
Documents issued in another state must be accompanied by notarized copies and translation into Russian, if there is a direct need for this.
The list of additional documentation is established by Order of the President of the Russian Federation No. 1325.
Diplomatic missions or consulates of foreign states are informed about the acquisition of Russian citizenship by their citizens.
Video: how to quickly become a Russian citizen under the program for the resettlement of compatriots
Submission of documents under a simplified procedure

There is a simplified procedure for obtaining Russian citizenship
When submitting an application and the necessary package of documents confirming the right to a simplified algorithm for obtaining citizenship, the applicant must contact the relevant government agency at the place of residence. For those living in Russia, this is the territorial representative office of the Migration Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. For those outside the territorial borders of the Russian Federation - a diplomatic or consular mission.
Having contacted the appropriate institution, a person must fill out an application of a certain form to acquire citizenship. This document is filled out personally, and in cases of physical disabilities of the person submitting the application - by an authorized person.
Submitting documents through another person or via mail is allowed in exceptional cases that are documented, and the package of documents provided is notarized.
The following documents are submitted along with the application (their final list will vary depending on the basis for the application of the “preferential” scheme):
- a document giving the right to reside in the territory of the state (residence permit);
- a certificate confirming the presence of income in our country (certificate of income, declaration, labor or employment certificate, pension certificate, etc.);
- birth certificate (including on the territory of the RSFSR or Russia);
- a document indicating sufficient proficiency in the state language (Certificate, document confirming education in Russia, the USSR or a country where Russian is the state language, etc.);
- a document confirming the renunciation of previous citizenship (application to the relevant government agencies of the relevant state with a postal receipt, etc.);
- marriage certificate with a citizen of the Russian Federation (provided for less than 3 years of married life);
- USSR passport;
- passport of a Russian citizen of one of the parents or children who have reached the age of majority;
- for those engaged in business in the country - an extract from the state register of entrepreneurs and a certificate of payment of taxes and fees to the budget for each year;
- for investors - an extract from the state register of entrepreneurs, the state register of securities owners, a certificate of payment of taxes and fees to the budget for each year;
- a document confirming the status of a WWII veteran;
- other documents.
The complete list of required documents is determined by the Regulations on the procedure for considering issues of citizenship of the Russian Federation (No. 1325 of November 14, 2002)
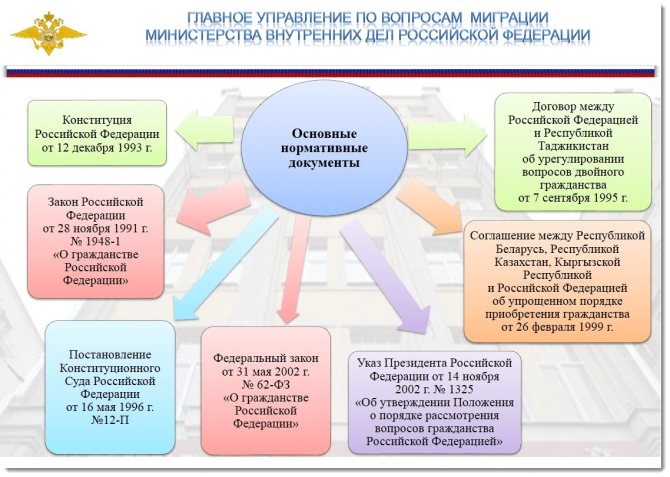
Basic regulatory documents
Requirements for renouncing existing citizenship of another state
The simplified procedure a priori assumes that the applicant renounces his previously held citizenship of another state. However, legal casuistry and literal interpretation of the provisions of the Law, according to lawyers, provide a “loophole” in this matter. Thus, the formulation “impossibility of refusal” for reasons that do not depend on the candidate, found in the text of the Law, leaves the possibility of “maneuver”.
At the same time, a number of leading lawyers note that this rule (on the renunciation of another citizenship) is contradictory. Since, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, dual citizenship is permissible.
However, we would like to draw your attention to the fact that in order to obtain Russian citizenship, a person must be ready to “break off” legal relations with the state he left (and, in many cases, such a “parting” is not always amicable). Therefore, any tricks associated with the reluctance to “part” with a passport of a foreign state suggest that a person’s desires to link his destiny with Russia are not always sincere.
Language test

Knowledge of the language is a must
Proficiency in oral (spoken) and written Russian is an indispensable condition for obtaining Russian citizenship. Does not depend on the procedure (regular or preferential) that is applied upon receipt.
A document confirming the required level of language proficiency is a Certificate. Issued after passing an exam (in the form of testing) at an educational institution that has the right to carry out such actions in accordance with the regulatory documents of the Ministry of Education. Testing is paid, the cost is about 5 thousand Russian rubles.
Also, knowledge of the history of Russia and the foundations of state and law is required.
Testing is not required if the applicant:
- received secondary, secondary specialized, higher, etc. education in Russia or educational institutions of the former USSR;
- was a citizen of a country, according to the legislation of which Russian was the national language;
- is a person of retirement age (65 years or more for men, for women - from 60 years).
Registration cost

Paperwork is not free
An applicant, when submitting an application for civil status, must keep in mind that the procedure itself involves payment for services. We will not dwell on the financial aspect of staying and living in our country. Let’s define a list of main areas that require financial expenditure:
- procedure for the official translation of a package of submitted documents from a foreign language into the state language of the Russian Federation;
- identification of the authenticity of provided documents - notary services;
- passing exams for basic proficiency in the state language of Russia;
- passing a medical examination;
- payment of duties required by law (about 3.5 thousand Russian rubles). If the applicant is refused, the funds paid will not be returned;
- other related expenses.
The above list is not exhaustive; unforeseen expenses may arise in the process, but it is unlikely to be reduced.
Simplified submission
Russian legislation also provides for the procedure for obtaining Russian citizenship in a simplified form.
Reasons for receiving
Persons who:
- have 1 or 2 parents who are citizens of the Russian Federation;
- had USSR citizenship, and now live in one of the former Soviet republics without having its citizenship;
- had USSR citizenship;
- are married to a citizen of the Russian Federation, provided that the marriage was concluded at least 3 years ago;
- have adult children who are citizens of the Russian Federation and recognized as incompetent - if the second parent died (or was deprived of parental rights);
- have children who are citizens of the Russian Federation if the second parent has died (or been deprived of parental rights);
- are engaged in business on the territory of the Russian Federation if the company has been operating in a certain field (the list is determined by the government) for at least 3 years, and the profit for these 3 years has exceeded 10 million rubles;
- paid at least 6 million rubles as tax to the Russian treasury;
- are highly qualified specialists (the list of professions is determined by the government and may vary depending on the region);
- are disabled and have children who are adult citizens of the Russian Federation.
List of documents
To obtain Russian citizenship in a simplified manner, a foreign person must collect the following package of documents:
- Application of the established form.
- Passport.
- Document from place of permanent residence
- Document confirming the change of surname (if it has changed).
- 3 photos.
Simplified procedure for changing citizenship for Russian speakers
One of the grounds on which Russian citizenship can be issued in a simplified manner is recognition as a native speaker of the Russian language.
The following persons can receive this status:
- Those who have reached 18 years of age.
- Those who speak Russian at a level sufficient for use in the family and everyday sphere.
- Those living in the territory of the Russian Federation or having a “direct” (parents, grandparents) relative who lived (or is living) in the territory of the Russian Federation.
To have the right to “benefits” when obtaining citizenship, as a native speaker of the Russian language, you must obtain a document confirming this status. To do this you need:
- Stay in the Russian Federation legally (have registration, temporary residence permit, residence permit).
- Submit an application for recognition as a native speaker of the Russian language. The application is submitted to the FMS office at the place of registration. It can be submitted no later than 15 days before the expiration of the legal period of stay. The date for the commission must be set within the next 2 days after submitting the application.
- Pass the exam to the commission, which makes a decision on assigning (or refusing) carrier status. The interview must be scheduled within the next 5 days after the application has been reviewed.
If a citizen successfully passes the exam, he should be given a confirmation within the next 5 days after passing.
After a foreign national has been recognized as a native speaker of Russian, this document can be used to speed up the procedure for changing citizenship. The next steps are as follows:
- An application is submitted to the migration service regarding the possibility of obtaining Russian citizenship.
- Apply for renunciation of current citizenship.
- Apply for Russian citizenship. In this case, the applicant must have registration and a residence permit.

The list of documents when applying for Russian citizenship under this scheme includes:
- Standard application form.
- International passport.
- Residence permit.
- Receipt for payment of state duty.
- 3 photos.
- Confirmation of the official source of income (bank statement with balance, work book, tax return, etc.).
- A document confirming the status of a native speaker (issued in case of successful passing of the exam).
- A document that confirms the renunciation of existing citizenship.
- A document confirming the change of surname (if any).
Additional factors that can speed up the receipt process (for citizens of Ukraine)
The procedure for obtaining Russian citizenship for Ukrainians is the same as for citizens of other states. However, they are subject to a list of exceptions and conditions under which the registration process can be significantly simplified.
The list is:
- Registration of political asylum.
- Official employment in regions remote from the capital.
- Buying a patent for work.
- Having relatives who are citizens of the Russian Federation.
- Participation in the “Compatriots” program (specially developed in 2014 due to military operations in Eastern Ukraine). Allows citizens of Ukraine to move to the regions of the Russian Federation provided for by the program: Voronezh, Tver regions, Karelia, Nenets, Siberian, Central, Far Eastern districts (to choose from).
Time frame for decision-making by government agencies
The deadlines for making a decision on conferring civil status are established by Article 35 of the Law. They range from 3 months to 1 year, depending on the procedure and the “benefits” of the applicant.
Table 2. Deadlines for making a decision for certain categories of applicants.
| State body (official) making the decision | Authorized authority in the field of migration (territorial missions), diplomatic and consular missions outside the country | Authorized authority in the field of migration (territorial missions), diplomatic and consular missions outside the country | The president |
| Acceptance procedure | Simplified | Simplified | General |
| The period from the moment the full package of documents is provided, during which a decision is made by the authorized body | no more than 3 months | no more than 6 months | No more than 1 year |
| Categories of applicants | Persons defined by paragraphs 2.1 and 7 of Article 14 of the Law (see paragraph 2.10 of Table 1) | Persons entitled to a simplified procedure, with the exception of those specified in paragraphs 2.1 and 7 of Article 14 | For all persons who do not have “benefits” |
Note. The results of consideration of applications can be sent to the candidate by postal notification, which, in turn, will increase the period of “real” receipt of the response by the applicant.
Refusal: what to do in this case
Russian authorities will deny citizenship in the following cases:
- using fake documents to obtain it,
- an attempt to become a Russian citizen using fictitious grounds,
- providing false information,
- information about the applicant’s affiliation with terrorism or extremism,
- civil service in another country,
- the applicant has socially dangerous diseases,
- lack of sufficient income or impossibility of confirming their legality.
A candidate for citizenship who has been refused may submit a letter of appeal addressed to the head of the migration authority. If you fail to appeal the refusal in this way, you can appeal to the court of first instance. It is advisable to use the services of a professional lawyer, this will increase the chances of success. Statistics show that courts recognize the illegality of the actions of the migration service in every third case.
Video: Illegal acquisition of citizenship by refugees
Features of receipt for residents of Ukraine

Ukrainians can also obtain Russian citizenship
Current legislation provides for the acquisition of Russian citizenship by citizens of neighboring Ukraine on “preferential” terms using a simplified procedure. The following have the right to take advantage of this opportunity:
- refugees. Persons who left the country due to the ongoing civil war, threat to personal safety and life;
- persons living in the territory of Crimea.
At the same time, candidates are not required to have a document indicating their renunciation of Ukrainian citizenship. When submitting documents, it is enough to attach a notarized letter to the authorized bodies of Ukraine, which contains a declaration of will on deprivation of Ukrainian citizenship.
Persons falling into the category of “refugees” must submit a corresponding application to the migration authorities within 24 hours of crossing the state border. After receiving this status, persons have the right to:
- temporary housing;
- allowance;
- medical care;
- assistance in finding a job;
- visits to educational institutions by minor children, etc.
In the first quarter of 2021, 61,189 people acquired Russian citizenship
- © Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation
On April 19, 2018, the Department of Internal Affairs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation published statistical data on the main indicators of activity on the migration situation in the Russian Federation for January-March 2021.
Let's take a look at some of them: 24 thousand 229 people arrived in the Russian Federation and were registered as compatriots and members of their families
— number of facts of registration of foreign citizens and stateless persons with migration registration 3.186.461
— issued work permits for foreign citizens and stateless persons in total 22.013
— highly qualified specialists 5217 including qualified specialists 2955
— issued work patents for foreign citizens and stateless persons 344.848
— submissions were sent regarding not allowing foreign citizens and stateless persons to enter the Russian Federation 71.338
61 thousand 189 people acquired citizenship of the Russian Federation
The breakdown by country of origin is interesting. From Abkhazia 39 people, Australia 1 person, Austria 2 people, Azerbaijan 2530 people, Algeria 4 people, Armenia 6235 people, Afghanistan 97 people, Bangladesh 5 people, Belarus 1014 people, Benin 1 person, Bulgaria 14 people, Bosnia and Herzegovina 7 people , Brazil 2 people, Great Britain 6 people, Hungary 1 person, Venezuela 1 person, Vietnam 87 people, Ghana 3 people, Germany 43 people, Greece 16 people, Georgia 525 people, Denmark 1 person, Egypt 31 people, Israel 30 people, India 12 people, Jordan 4 people, Iraq 3 people, Iran 10 people, Spain 6 people, Italy 20 people, Yemen 10 people, Kazakhstan 10257 people, Cameroon 3 people, Kenya 1 person, Kyrgyzstan 2212 people, China 19 people, Congo 2 people , Republic of Congo 2 people, Republic of Korea 1 person, Cuba 5 people, Latvia 32 people, Lebanon 6 people, Lithuania 35 people, Macedonia 3 people, Morocco 8 people, Moldova 3784 people, Mongolia 3 people, Nepal 1 person, Nigeria 5 people , Netherlands 2 people, Pakistan 6 people, Palestine 4 people, Peru 2 people, Poland 5 people, Romania 3 people, Senegal 1 person, Serbia 27 people, Syria 89 people, Slovakia 1 person, Slovenia 1 person, USA 27 people, Tajikistan 7797 people, Thailand 1 person, Tunisia 10 people, Turkmenistan 115 people, Uzbekistan 4962 people, Ukraine 19427 people, France 18 people, Croatia 1 person, Montenegro 1 person, Czech Republic 2 people, Sweden 1 person, Ecuador 1 person, Estonia 7 people , South Ossetia 11 people, stateless people 1326 people, non-citizens of Latvia 2 people, other countries 4 people.
Reasons for refusal

There are a number of reasons for refusal
Submitting the required document package does not guarantee automatic receipt of “citizen” status. Legislation provides for restrictions for a certain circle of persons for whom it is impossible to grant Russian citizenship.
The blacklist includes people who:
- carry out actions that pose a threat to our country;
- agitate or take actions aimed at a violent change of the constitutional system;
- took part in armed conflicts on the territory of other countries against the Russian armed forces sent there as peacekeepers;
- committed terrorist attacks (took part in their development, support) against citizens of the Russian Federation, government agencies, both on the territory of the country and abroad;
- took part in illegal, extremist acts, for which criminal liability is provided in Russia;
- are persons whose stay on the territory of the country is undesirable (by decision of the authorized body) or for whom there is an entry restriction;
- are persons with an outstanding criminal record, are being prosecuted by Russian law enforcement agencies, and are serving sentences in prison.
- are military personnel of the army of a foreign state (serving in law enforcement agencies or internal security, intelligence, etc.).
In addition, grounds for refusal may include:
- provision of documents whose data is untrue or false;
- taking the oath.
If a refusal is received, a person has the opportunity to:
- challenge the decision in court;
- submit a second application for citizenship (no earlier than 1 year after the previous decision).
In the absence of legally established restrictions prohibiting a person’s presence on the territory of the country, he has the right to stay in Russia. To do this, you must obtain the appropriate permission from the migration service (a mark is placed on the migration card).
Grounds for obtaining citizenship in the standard way
There is a certain list of grounds by which you can acquire Russian citizenship using the standard procedure. Let's look at them in more detail.
Family bonds
You can move to the territory of the Russian Federation and subsequently obtain citizenship if close relatives who have the status of citizens of the Russian Federation live on its territory. From a legal point of view, close relatives are considered to be children and parents, blood brothers and sisters, and grandparents.
Foreigners have the opportunity to move to the Russian Federation and begin the immigration process if they provide the immigration service with an invitation from the Russian side. Inviting relatives must draw up a written guarantee for those moving, in which they undertake to provide them with shelter and the necessary financial assistance (if circumstances require), and also to facilitate the integration of those moving into Russian society.
Relocating relatives will first receive a temporary residence permit, and then move on to the next steps of the immigration process, after which they will be able to request Russian citizenship.
Video: the easiest ways to obtain Russian citizenship
Marriage with a Russian citizen
When marrying citizens of the Russian Federation, foreign spouses have the right to obtain citizenship through an accelerated procedure. To do this, they need to live in an official marriage for at least three years on the territory of the Russian Federation. In the country they will have the status of temporary residents.
Before submitting an application for citizenship, the foreign life partner of a Russian citizen must demonstrate a sufficient level of proficiency in the Russian language, as well as confirm deep integration into Russian society. Obtaining citizenship will not pose a particular problem if the foreign spouse has not violated Russian legislation for three years and, of course, if the marriage is not dissolved. Official dissolution of the marriage during the period preceding the request for citizenship means that the foreign spouse will lose all rights to obtain it expeditiously.
The marriage certificate must comply with Russian standards. If the marriage took place abroad, the document will require legalization in accordance with Russian law.
If employees of the Russian migration service prove that the marriage union is fictitious, this will lead to the leveling of all its legal consequences. A foreign participant in a conspiracy to obtain Russian citizenship by fraudulent means will be deported from the Russian Federation within two weeks.

When marrying citizens of the Russian Federation, foreign spouses have the right to obtain citizenship through an accelerated procedure
Investment activities and business
Representatives of foreign business circles who have certain business assets abroad can move their activities to the territory of the Russian Federation. If it is found to be effective and cost-effective, as well as useful for the development of the country, then they have the right to obtain citizenship on preferential terms. Strictly speaking, this will not be a simplified procedure, but citizenship in this way can be obtained in just three years. The opportunity to take advantage of preferential conditions exists for entrepreneurs who generate at least 10 million rubles of taxable profit over a three-year period.
Registration of your own enterprise is not a prerequisite. A foreign businessman can buy an already established business. But in this case, there is a minimum investment threshold of 10 million rubles.

The opportunity to take advantage of preferential conditions for obtaining citizenship exists for entrepreneurs who, over a three-year period, generate at least 10 million rubles of taxable profit
Changes are constantly being made to Russian citizenship legislation. We can see their appearance in 2012, 2015, 2021 and 2018. It can be stated that Russian legislators are trying to keep up with the times, responding to relevant challenges in a timely manner. But personally, I observe a certain confusion among those wishing to become Russian citizens in connection with innovations. Sometimes they are guided by outdated versions of the law, so they take the wrong steps or miss the right opportunities. And immigration officials provide consultations to citizenship applicants only upon their request. Therefore, advice: you should carefully monitor changes in migration laws.
Citizenship for refugees
Migrants who were forced to leave their homeland due to hostilities, political persecution, or persecution for belonging to a particular religion or national group will be able to apply for refugee status on Russian territory. The Russian authorities will issue it to those forced migrants who, according to Russian legislation and international standards, will be recognized as persons whose lives and the lives of their family members are in objective danger in their homeland.
Persons with refugee status will be able to request Russian citizenship after five years of residence in Russia. Previously, the Russian authorities will monitor the situation developing at that time in the homeland of the refugees. If a decision is made that it is not safe for them to return to their native land, then yesterday’s refugees become candidates for Russian citizenship.
Special cases of assignment of Russian citizenship
Special cases of assignment of Russian citizenship do not belong to either the simplified procedure or the general one. They can be considered as a separate category.
In special cases, Russian citizenship is assigned to foreign citizens who have made a significant contribution to the protection of Russian interests in the international political arena, world-class athletes who performed under the Russian flag, foreign scientists, and representatives of the art world. Such categories of foreigners will be granted Russian citizenship only on the basis of a separate government order. There are no additional conditions for them.
In this situation, the initiative to obtain or issue citizenship can be taken by both parties: a foreign citizen or representatives of the Russian authorities.

Gerard Depardieu received a Russian passport under special conditions










